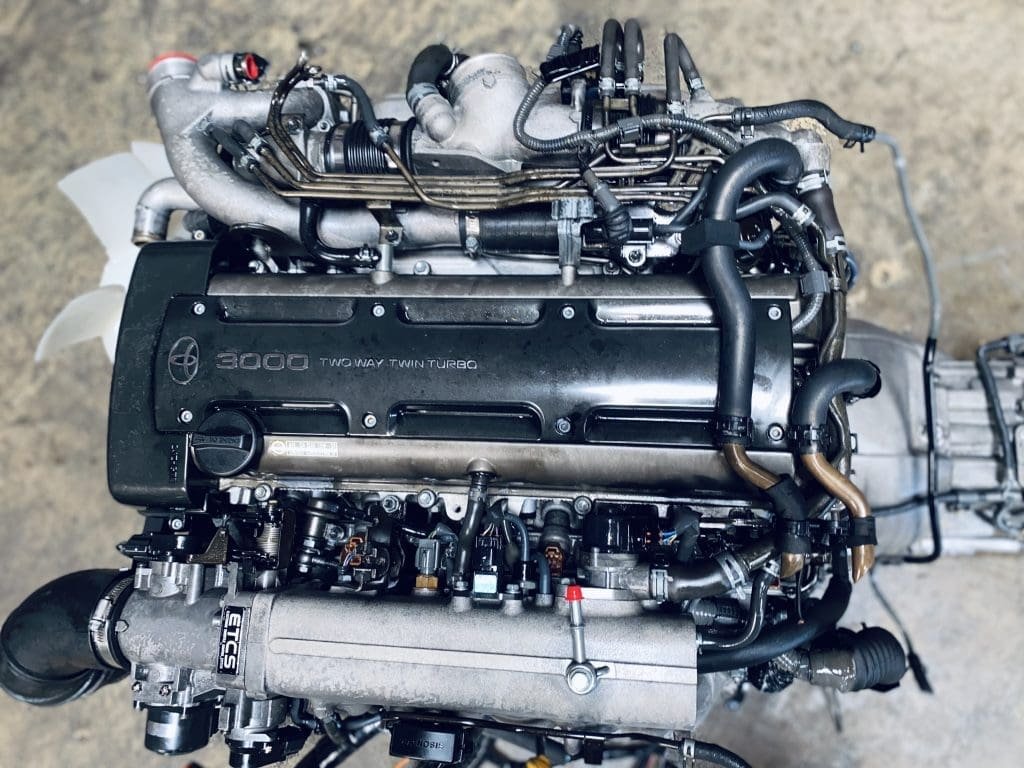
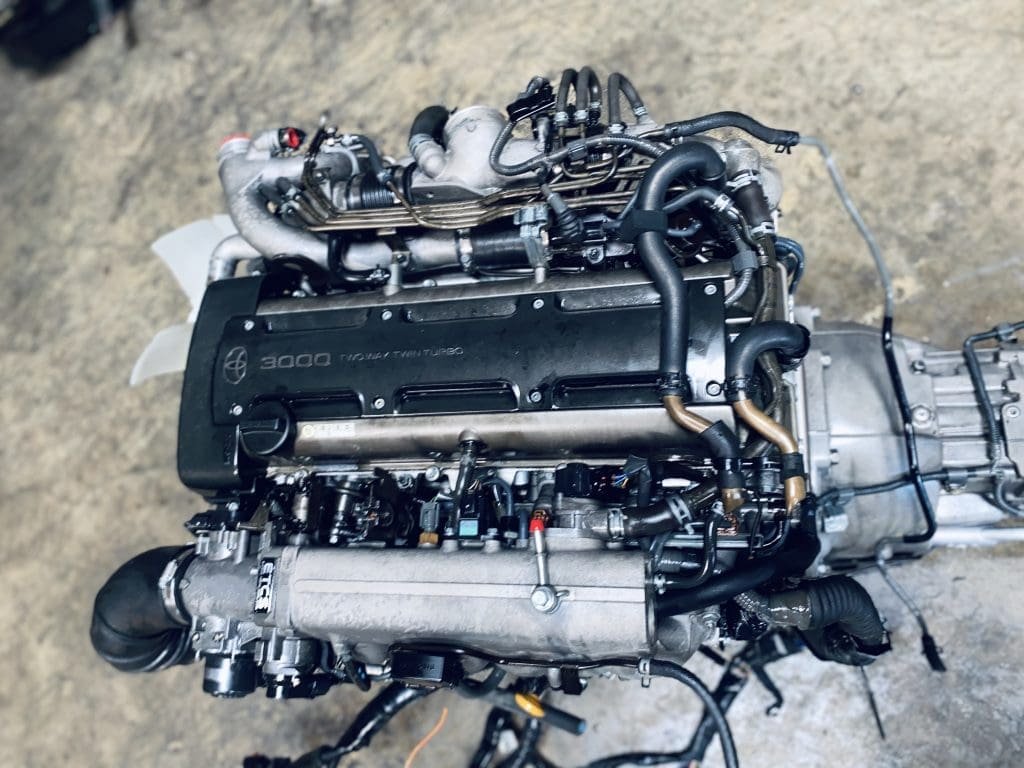
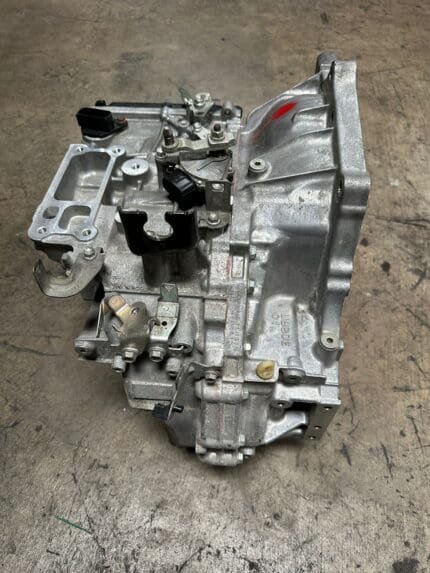
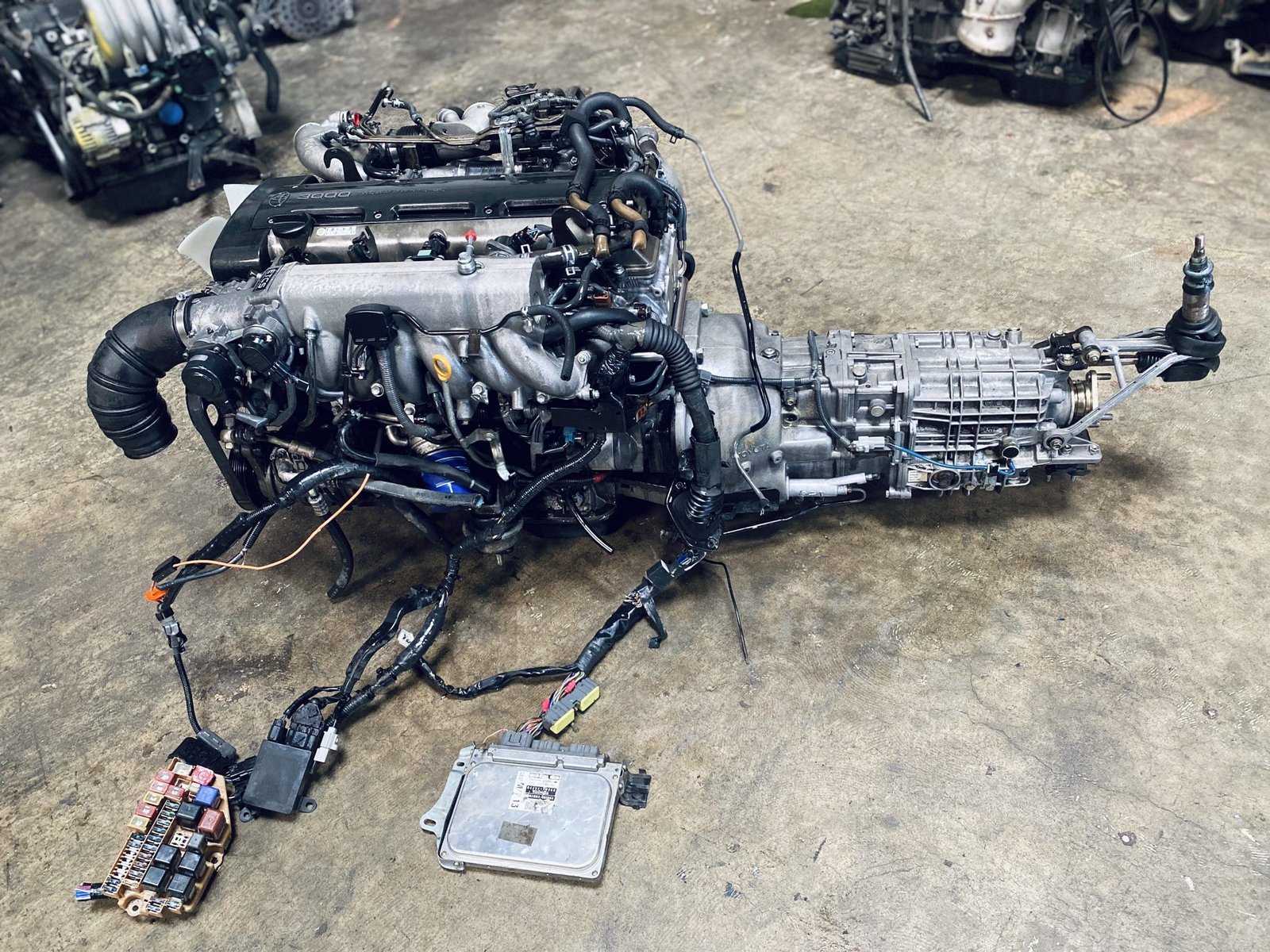
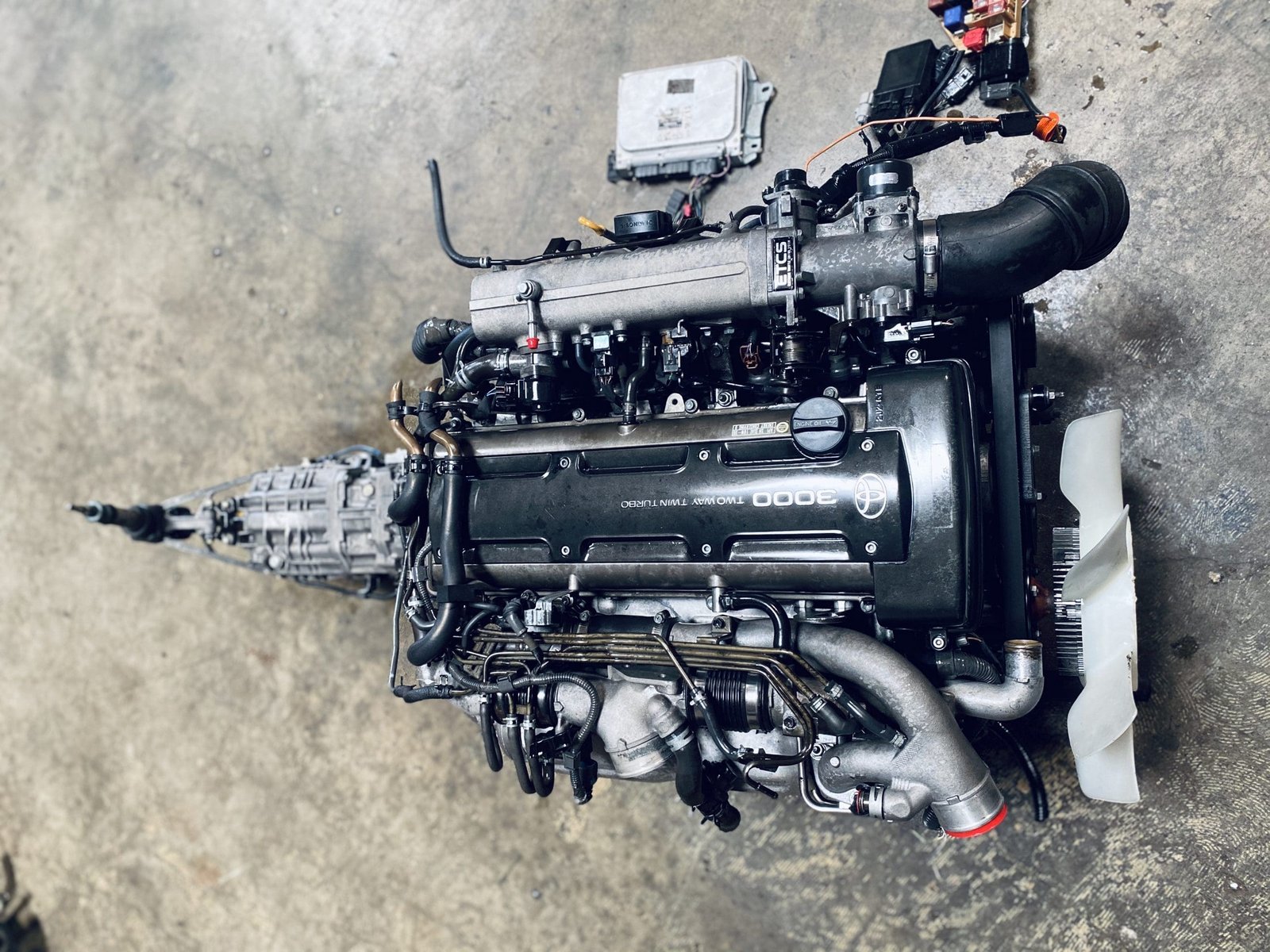
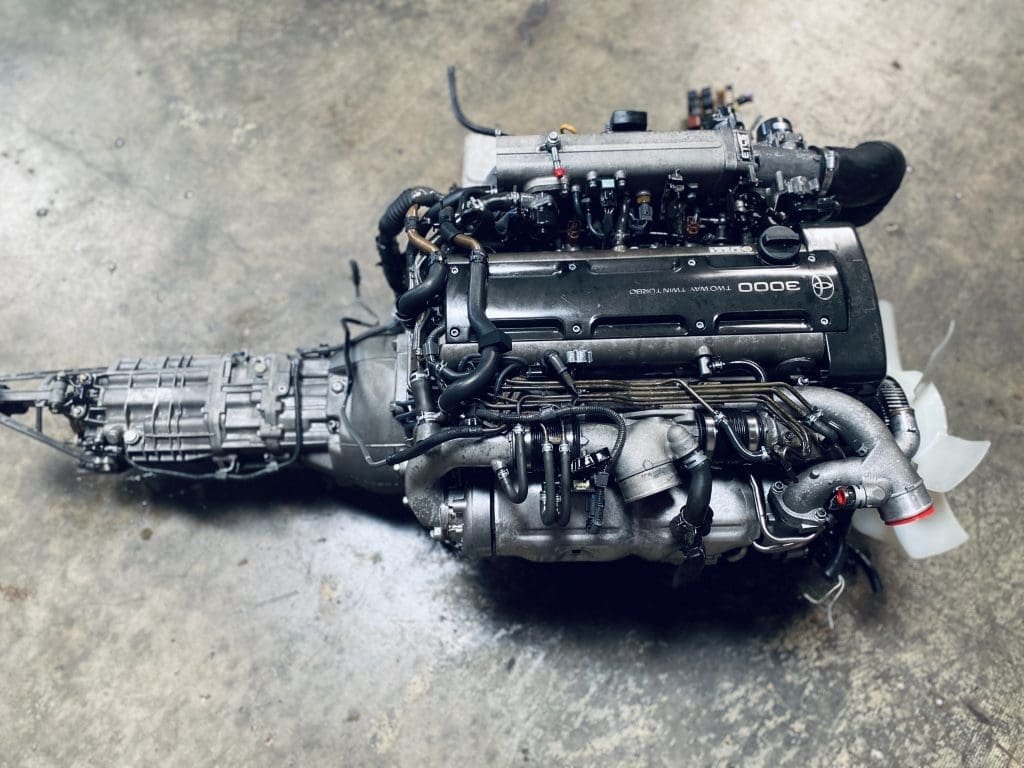
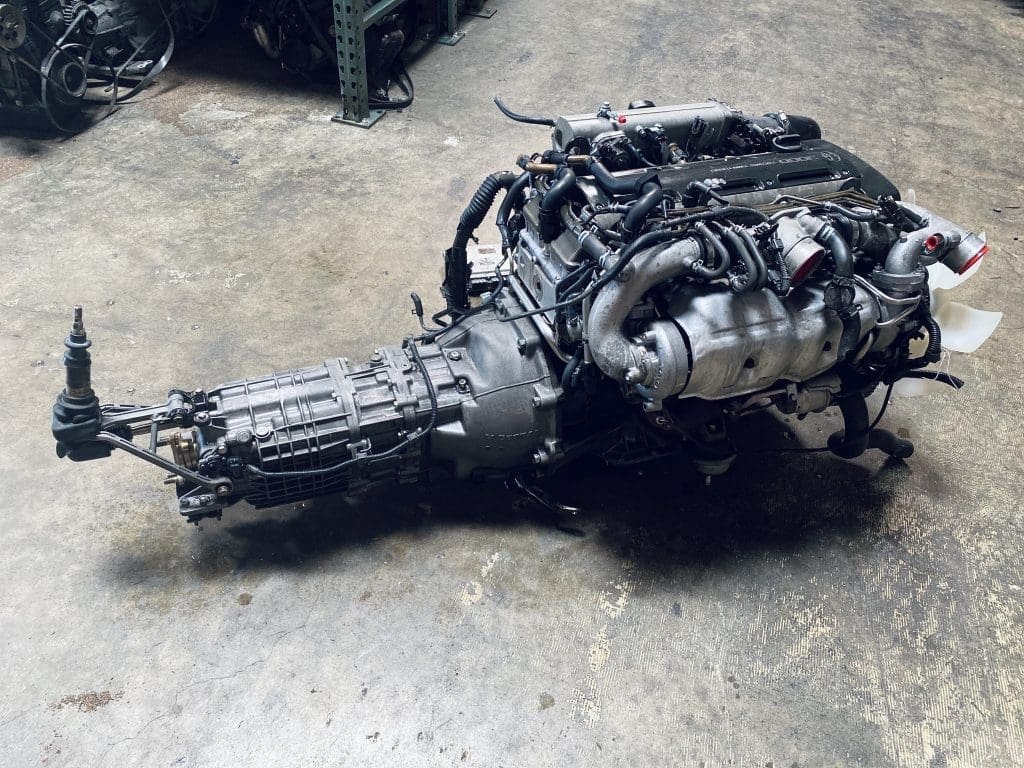
2JZGTE Non-VVTi Twin Turbo Rear Sump 3.0L Engine with V160 Getrag 6 Speed Manual Transmission MK4 JZA80 Toyota Supra
Buy 2JZGTE Non-VVTi Twin Turbo Rear Sump 3.0L Engine with V160 Getrag 6 Speed Manual Transmission MK4 JZA80 Toyota Supra for sale online. The 2JZGTE Non-VVTi engine is a marvel of engineering that has become an icon among car enthusiasts and tuners worldwide. Known for its robust construction, immense power potential, and adaptability, this twin-turbocharged inline-six engine from Toyota has carved out a legendary reputation in the world of high-performance engines. This article provides an in-depth overview of the 2JZGTE Non-VVTi twin-turbo rear sump engine, its features, benefits, applications, and answers to frequently asked questions.
Overview
The 2JZGTE Non-VVTi engine belongs to Toyota’s renowned JZ series, a family of inline-six engines developed for high performance and reliability. Introduced in the early 1990s, the 2JZGTE became the performance standard for vehicles like the Toyota Supra MKIV and other high-powered Toyota models. The Non-VVTi variant represents the earliest version of the engine, devoid of Toyota’s Variable Valve Timing technology, resulting in a simpler yet highly tunable powerplant.
Key Specifications:
- Engine Type: Inline-6 DOHC, turbocharged
- Displacement: 3.0L (2997cc)
- Bore x Stroke: 86 mm x 86 mm
- Compression Ratio: 8.5:1
- Induction System: Twin sequential turbochargers
- Fuel System: Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI)
- Oil System: Rear sump configuration
- Max Factory Output: Approximately 276 hp and 318 lb-ft torque (Japanese factory rating, often understated)
Features of the Non-VVTi 2JZGTE Engine
- Iron Block Construction: The iron block of the 2JZGTE is one of its standout features. Known for its durability, it can handle immense power outputs, making it ideal for aftermarket tuning.
- Twin Sequential Turbos: The Non-VVTi 2JZGTE uses a sequential twin-turbo setup. At lower RPMs, a single turbo is active to reduce lag, and as the RPMs increase, the second turbo engages, ensuring smooth and consistent power delivery.
- Rear Sump Configuration: The rear sump oil pan layout is particularly advantageous for swaps into vehicles with specific chassis constraints, such as certain sports cars and compact trucks.
- Non-VVTi Simplicity: Without Variable Valve Timing (VVTi), the engine offers simplicity in tuning and modifications. This is especially appealing for those seeking ultimate control over engine parameters.
- High Aftermarket Support: The 2JZGTE Non-VVTi enjoys unparalleled aftermarket support, with parts ranging from upgraded turbos to standalone engine management systems readily available.
Applications
The 2JZGTE Non-VVTi engine is versatile and widely used in various automotive projects:
- Toyota Supra MKIV (A80): The original home of this engine, where it gained its legendary status.
- Engine Swaps: A popular choice for swapping into vehicles such as Nissan 240SX, Mazda RX-7, BMW E36/E46, and other platforms.
- Drag Racing: With minimal modifications, the engine can produce over 1,000 hp, making it a staple in the drag racing community.
- Drifting: The linear power delivery and reliability of the 2JZGTE make it an excellent option for professional drift cars.
Benefits of the Rear Sump Configuration
- Chassis Fitment: The rear sump design is essential for vehicles with crossmember locations that interfere with front sump layouts.
- Balance and Clearance: Improved weight distribution and clearance for custom builds.
- Oil Management: Optimized for performance in rear-wheel-drive applications, ensuring consistent oil delivery during high G-forces.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the difference between the Non-VVTi and VVTi versions of the 2JZGTE? The main difference lies in the presence of Toyota’s Variable Valve Timing (VVTi) in the latter version. VVTi enhances efficiency and torque at lower RPMs, but the Non-VVTi is favored by tuners for its simplicity and higher RPM tuning potential.
Q2: How much power can a stock 2JZGTE Non-VVTi handle? The stock internals of a 2JZGTE Non-VVTi are capable of handling approximately 600-700 horsepower with proper tuning. Upgraded components can push this limit to over 1,000 horsepower.
Q3: What fuel system upgrades are recommended for higher horsepower builds? To achieve higher power levels, upgrades like larger fuel injectors, a high-flow fuel pump, and an aftermarket fuel pressure regulator are recommended.
Q4: Is the rear sump configuration suitable for all vehicles? No, the rear sump configuration is specifically beneficial for vehicles with rear subframes or crossmembers that conflict with a front sump design. It’s essential to verify compatibility with the intended chassis.
Q5: What are common turbo upgrade paths for the 2JZGTE Non-VVTi? Popular turbo upgrades include:
- Single Turbo Conversion: Replacing the twin turbos with a large single turbo for simplified plumbing and higher peak power.
- Upgraded Twin Turbos: Retaining the twin-turbo setup but using higher-flow units for enhanced performance.
Q6: What transmission options work well with the 2JZGTE Non-VVTi? The Toyota R154 and Getrag V160/V161 6-speed manual transmissions are commonly paired with the 2JZGTE. For higher horsepower builds, aftermarket transmissions such as the TREMEC T56 or sequential gearboxes are viable options.
Q7: How does the Non-VVTi engine perform in motorsport? The 2JZGTE Non-VVTi is a favorite in drag racing, drifting, and time attack events due to its reliability, tunability, and high power output potential.
Conclusion
The 2JZGTE Non-VVTi twin-turbo rear sump 3.0L engine remains a hallmark of automotive engineering. Its robust construction, flexibility, and incredible power potential make it a top choice for performance enthusiasts and professional racers alike. Whether you’re building a street machine, a race car, or a showpiece, the 2JZGTE Non-VVTi is a legendary powerplant worthy of consideration.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.